Machine Learning: A Beginner’s Guide to AI-Powered Automation
Machine learning (ML) is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables computers to learn from data and improve performance without being explicitly programmed. ML powers technologies like chatbots, recommendation systems, and self-driving cars.
Discover more at RedSysTech Machine Learning Guide.
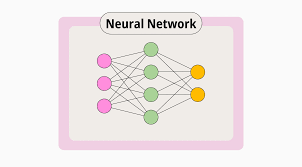
What is Machine Learning?
- Machine learning is a data-driven AI approach where systems identify patterns and make predictions.
- Uses statistical models, algorithms, and neural networks.
- Key applications include image recognition, speech processing, and predictive analytics.
Learn more at Machine Learning Basics.
How Machine Learning Works
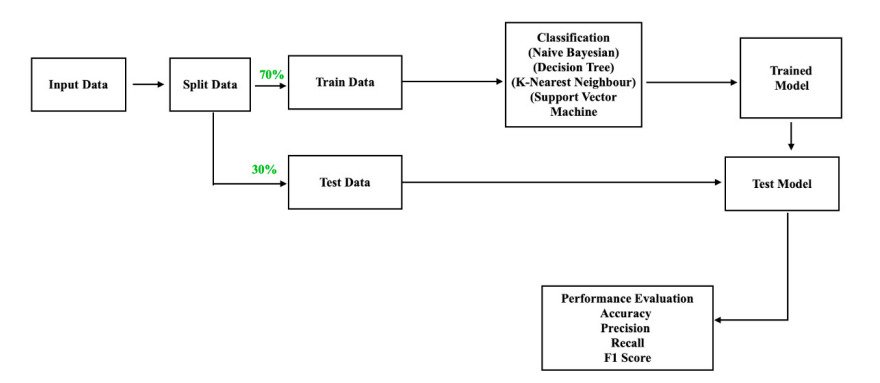
1. Data Collection & Preprocessing
- Gather and clean structured or unstructured data.
2. Algorithm Selection
- Choose models based on the problem (classification, regression, clustering).
3. Training the Model
- The model learns patterns from labeled data.
4. Testing & Deployment
- Evaluate the model before deploying it in real-world applications.
Explore How Machine Learning Works.
Types of Machine Learning
| Type | Description | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Supervised Learning | Learns from labeled data | Spam detection, Image recognition |
| Unsupervised Learning | Finds patterns in unlabeled data | Customer segmentation, Anomaly detection |
| Reinforcement Learning | Learns through rewards & feedback | Self-driving cars, Robotics |
Check out Types of Machine Learning.
Common Machine Learning Algorithms
- Linear Regression – Predicts numerical values (house prices, sales forecasting).
- Decision Trees – Used in classification problems like fraud detection.
- Neural Networks – Powers deep learning applications such as face recognition.
- Support Vector Machines (SVMs) – Separates data into categories efficiently.
Applications of Machine Learning
1. Healthcare
- AI-driven disease diagnosis and drug discovery.
2. Finance & Banking
- Fraud detection, risk assessment, and automated trading.
3. E-Commerce & Marketing
- Product recommendations (Amazon, Netflix, YouTube).
4. Autonomous Systems
- Self-driving cars, smart assistants, and robotics.
Check out AI & Machine Learning in Industries.
Machine Learning vs Deep Learning vs AI
| Feature | Machine Learning | Deep Learning | Artificial Intelligence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses data to learn patterns | Uses neural networks for complex tasks | Simulates human intelligence |
| Computational Power | Moderate | High | Varies |
| Use Cases | Predictive analytics | Self-driving cars | General automation |
Challenges in Machine Learning
- Data Quality Issues – Poor data leads to inaccurate models.
- Overfitting & Underfitting – Model learns too much or too little from training data.
- Computational Power – Training large ML models requires high-performance hardware.
- Ethical Concerns – Bias in AI models can impact fairness and decision-making.
Explore Machine Learning Challenges.
Future of Machine Learning
- AI-Powered Automation – ML will enhance self-learning AI models.
- Explainable AI (XAI) – Making ML models more transparent.
- Federated Learning – Privacy-focused AI training across multiple devices.
- Quantum Machine Learning – Faster computing for complex AI problems.
Read about The Future of AI & Machine Learning.
Conclusion
- Machine learning is revolutionizing industries by enabling data-driven decision-making.
- It powers AI applications like self-driving cars, chatbots, and recommendation engines.
- The future of ML includes more automation, ethical AI, and advanced computing techniques.
Start exploring Machine Learning Today.