Quantum Computing: The Future of High-Speed Computing
Quantum computing is revolutionizing the way we process information. Unlike classical computers that rely on bits (0s and 1s), quantum computers use qubits to perform complex calculations exponentially faster.
Explore more at Red9SysTech Quantum Computing Guide.
What is Quantum Computing?
- Quantum computing is a cutting-edge field that uses quantum mechanics to process information.
- Unlike classical computers, quantum computers leverage superposition and entanglement for parallel computing.
- These computers can solve problems in seconds that would take traditional computers years.
Learn more about Quantum Computing Basics.

How Does Quantum Computing Work?
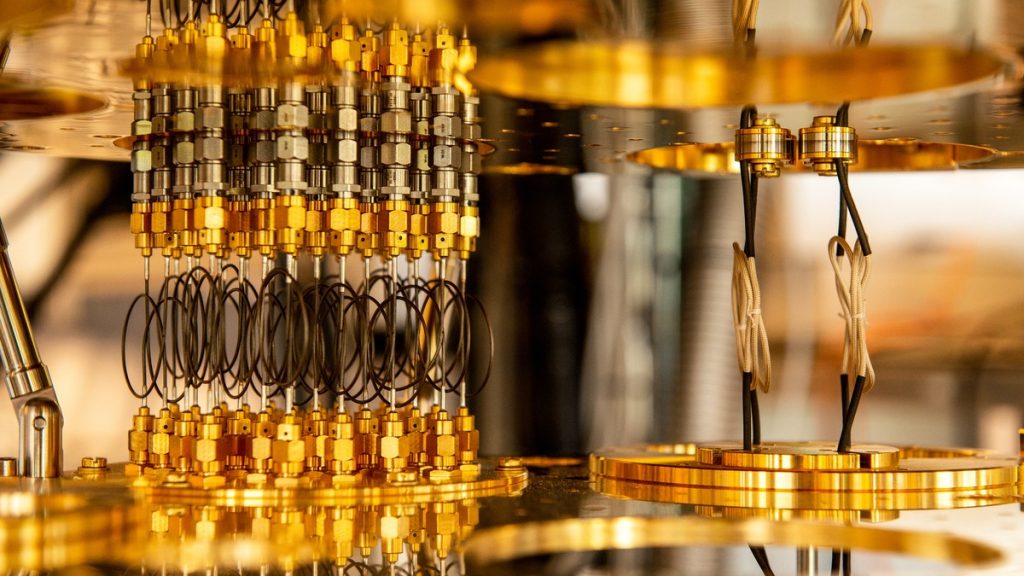
1. Qubits – The Foundation of Quantum Computing
- Unlike classical bits (which are either 0 or 1), qubits exist in multiple states at once (superposition).
- Example: A single qubit can be in both 0 and 1 simultaneously.
2. Superposition – Multiple States at Once
- Classical computers compute one step at a time, while quantum computers process multiple possibilities simultaneously.
3. Entanglement – Quantum Connectivity
- When two qubits become entangled, changing the state of one instantly affects the other, no matter the distance.
- This enables ultra-fast communication and problem-solving.
Read more on How Qubits Work.
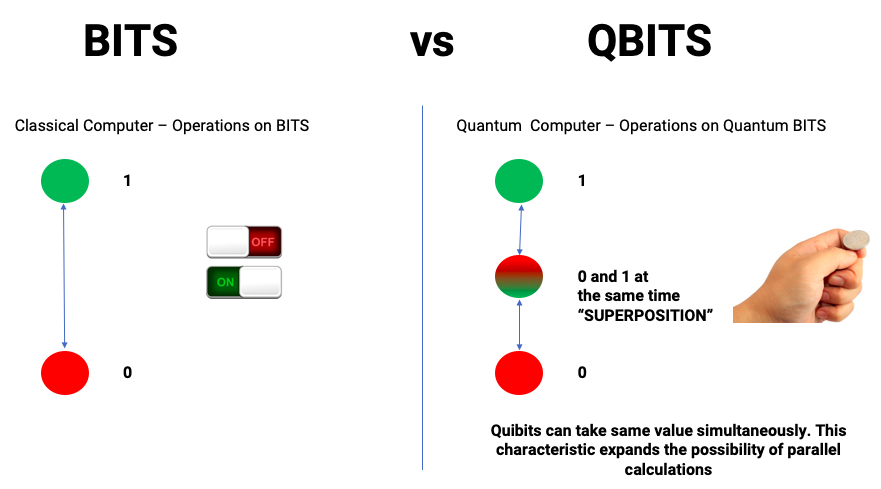
Applications of Quantum Computing
1. Cryptography & Cybersecurity
- Quantum computers can break traditional encryption algorithms in seconds.
- Scientists are developing quantum-resistant encryption to protect data.
2. Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
- Faster pattern recognition, optimization, and deep learning models.
- Improves AI’s ability to process large datasets quickly.
3. Drug Discovery & Healthcare
- Simulates molecular structures to develop new medicines faster.
- Helps in protein folding and genetic analysis for precision medicine.
4. Financial Modeling & Risk Analysis
- Quantum algorithms improve financial predictions and stock market analysis.
- Used by banks for fraud detection and portfolio optimization.
Discover Real-World Quantum Applications.
Challenges of Quantum Computing
1. Hardware Limitations
- Quantum computers require extreme cooling (near absolute zero) to function.
- Still in the experimental phase, making it expensive to develop.
2. Error Correction & Stability
- Qubits are fragile and prone to errors due to decoherence.
- Scientists are working on quantum error correction methods.
3. Accessibility & Cost
- Currently, quantum computing is limited to research labs and tech giants.
- Cloud-based quantum computing (IBM, Google, Microsoft) is making it more accessible.
Read more on Challenges in Quantum Computing.

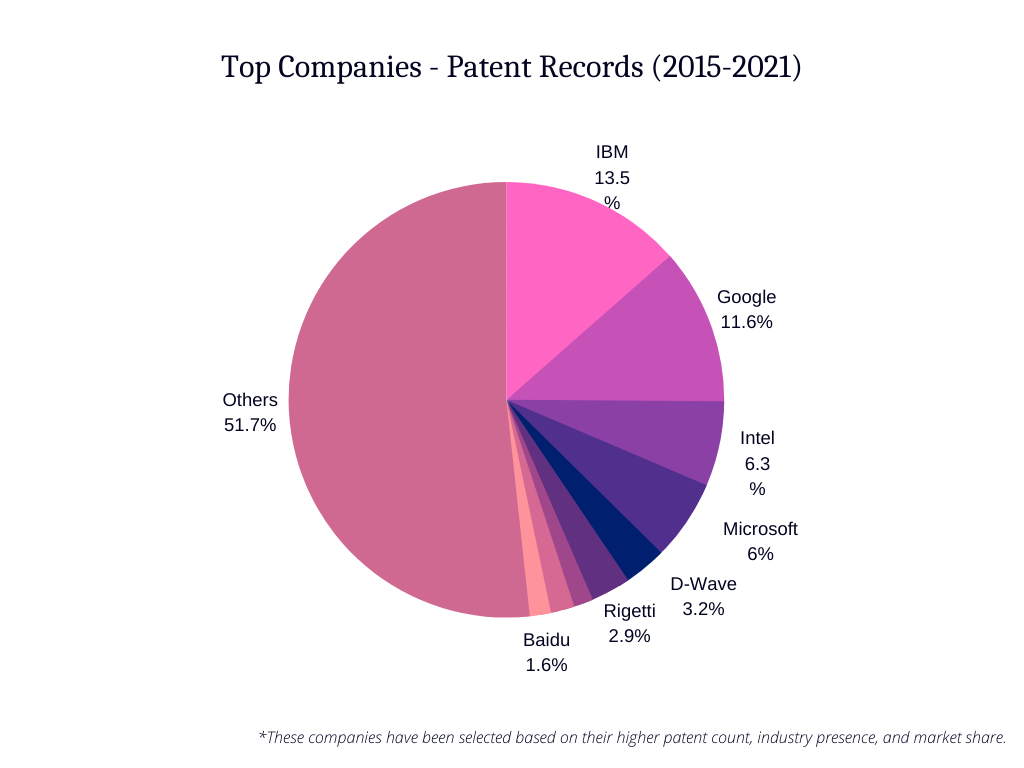
Leading Companies in Quantum Computing
1. IBM Quantum
- Developed IBM Q System One, a commercial quantum computer.
2. Google Quantum AI
- Achieved quantum supremacy with its Sycamore processor.
3. Microsoft Azure Quantum
- Provides cloud-based quantum computing access.
4. D-Wave Systems
- Focuses on quantum annealing for optimization problems.
Learn more about Top Quantum Computing Companies.
The Future of Quantum Computing
- Quantum computing will revolutionize AI, cybersecurity, and medicine.
- Companies like Google, IBM, and Microsoft are investing in quantum research.
- Within the next decade, quantum computers will become more powerful and accessible.
Stay updated with Quantum Computing Trends.

Conclusion
- Quantum computing is the next frontier in high-speed computing.
- It has potential applications in AI, cryptography, finance, and healthcare.
- Although still in development, quantum computing is advancing rapidly.
Start exploring Quantum Computing Today.