Blockchain Technology – The Future of Secure Digital Transactions
Blockchain technology is transforming industries by eliminating intermediaries, improving transparency, and securing transactions. Originally developed for cryptocurrencies, it is now being applied in finance, healthcare, supply chain, and beyond.
Explore more at Red9Systech Blockchain Guide.
What is Blockchain Technology?
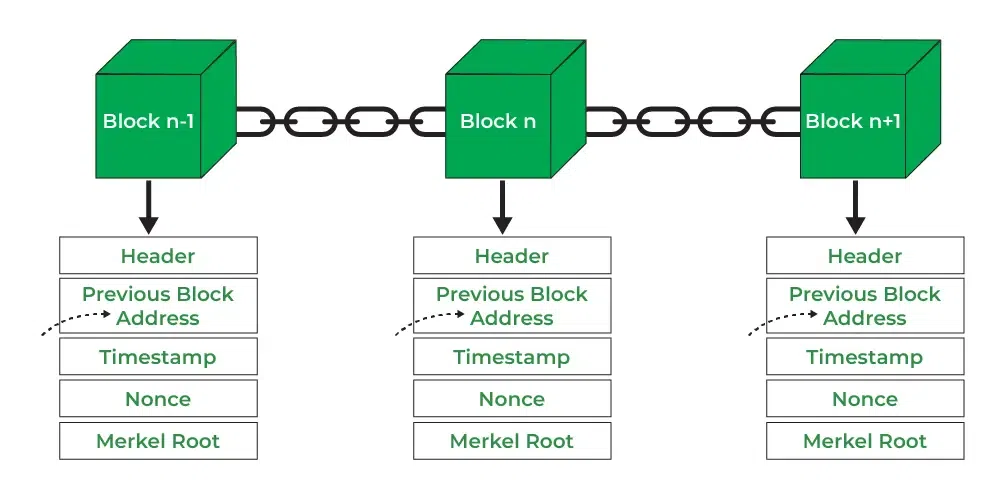
- Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions securely and transparently.
- Data is stored in blocks that are linked using cryptographic hashes, forming a chain.
- It eliminates the need for a central authority, making transactions tamper-proof.
🔗 Learn more at IBM’s Blockchain Guide.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain technology operates using a series of steps that ensure security, transparency, and efficiency.
1. Transaction Initiation
A user initiates a transaction (e.g., sending cryptocurrency or verifying a contract).
2. Block Creation
The transaction is grouped with others into a block.
3. Consensus Mechanism
Blockchain networks validate the transaction using methods such as:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Miners solve complex puzzles to validate transactions.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators are chosen based on their stake in the network.
4. Block Addition & Security
Once verified, the block is added to the blockchain, ensuring permanent and tamper-proof records.)
Read more about How Blockchain Works
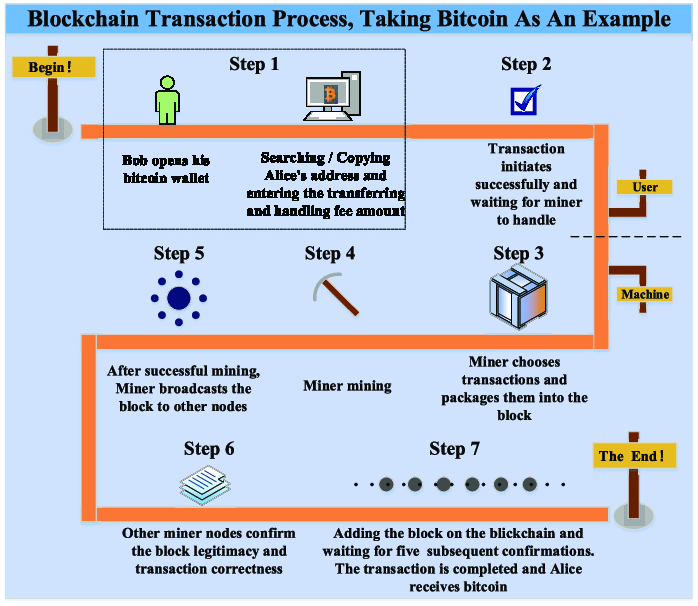
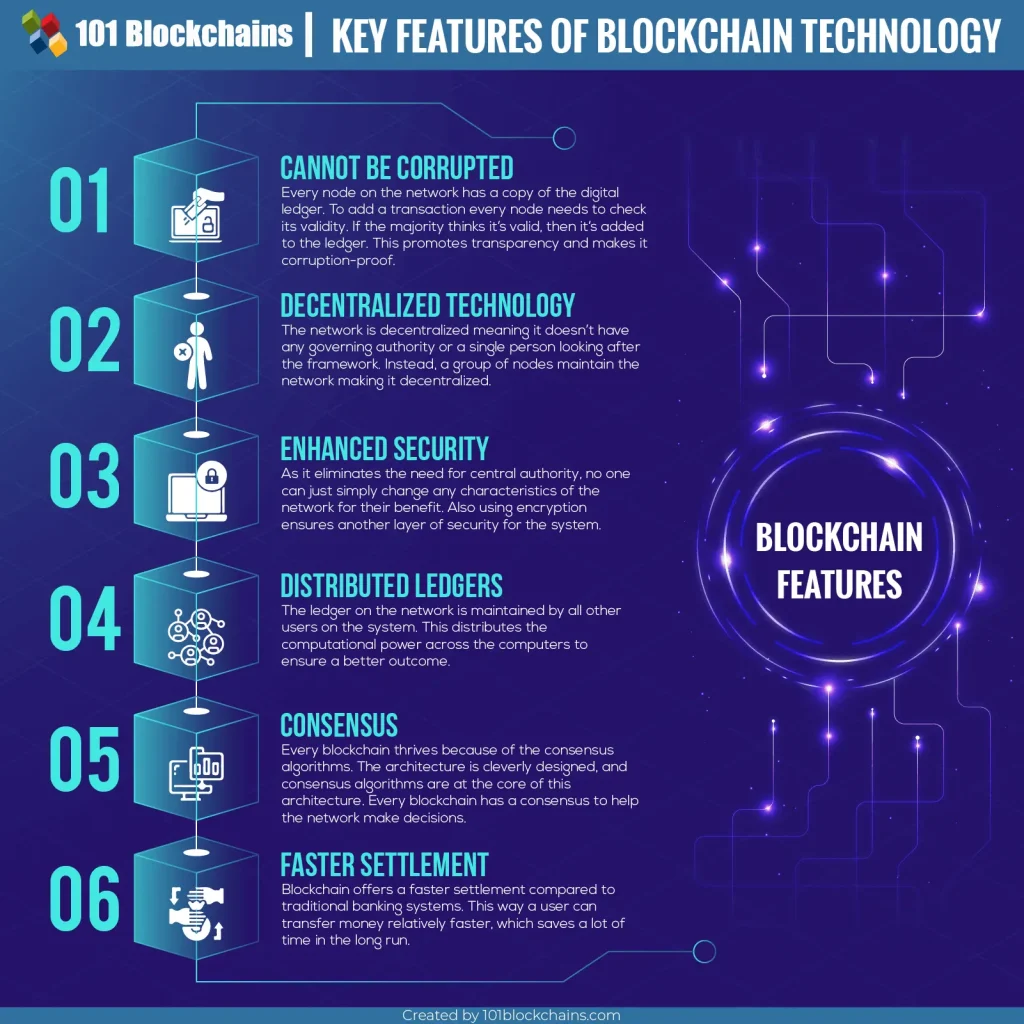
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
Feature Description Decentralization No central authority controls the data. Immutability Once recorded, data cannot be altered. Transparency Transactions are visible to all network participants. Security Uses cryptography to protect data. Learn about Blockchain’s Core Features.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
- Automates transactions without intermediaries.
- Ensures tamper-proof property records.
1. Cryptocurrencies & Finance
- Enables secure peer-to-peer transactions (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum).
- Used for cross-border payments and decentralized finance (DeFi).
2. Supply Chain Management
- Ensures end-to-end visibility of goods movement.
- Reduces fraud, counterfeiting, and inefficiencies.
3. Healthcare
- Stores electronic health records securely.
- Enhances patient data sharing among hospitals.
4. Smart Contracts & Real Estate
Read about Blockchain Use Cases.

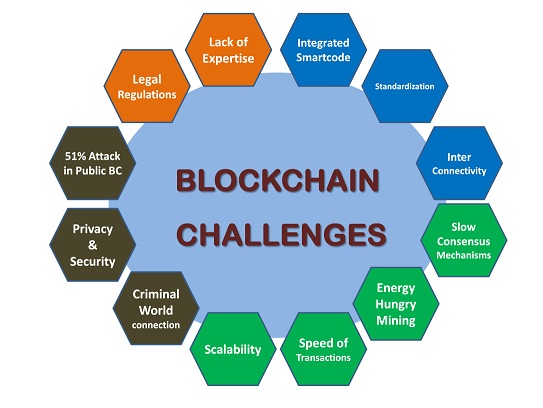
Challenges of Blockchain Technology
1. Scalability Issues
- Limited transaction processing speed in public blockchains.
2. High Energy Consumption
- Proof of Work (PoW) mining requires significant computing power.
3. Regulatory Uncertainty
- Governments are still developing legal frameworks for blockchain adoption.
📌 Image Placement: (Insert an image depicting blockchain challenges like energy usage and regulation.)
🔗 Learn more about Blockchain Challenges & Solutions.
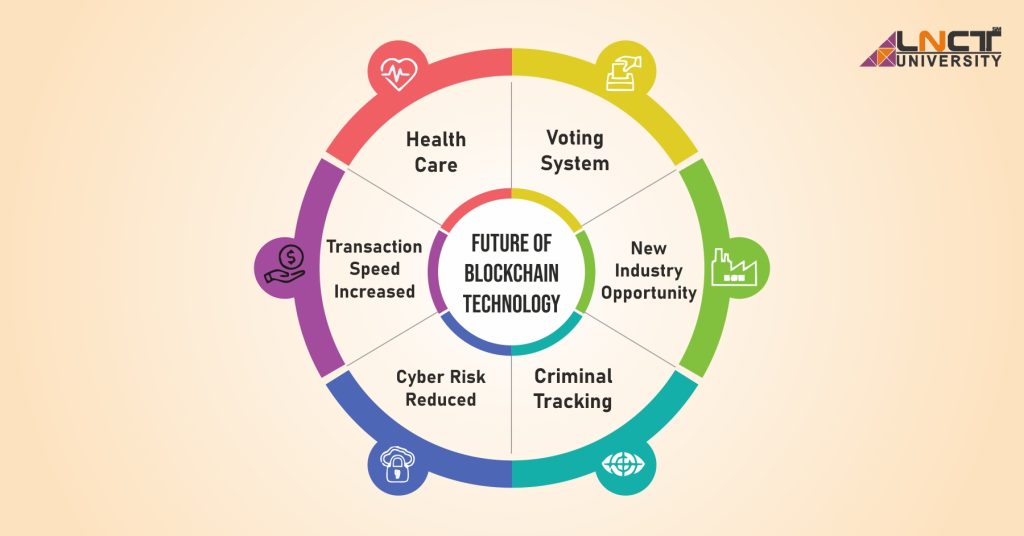
The Future of Blockchain Technology
- Interoperability between blockchains will improve seamless transactions.
- Hybrid blockchain models will enhance business adoption.
- AI & blockchain integration will boost security and automation.
Stay updated with Blockchain Trends
Conclusion
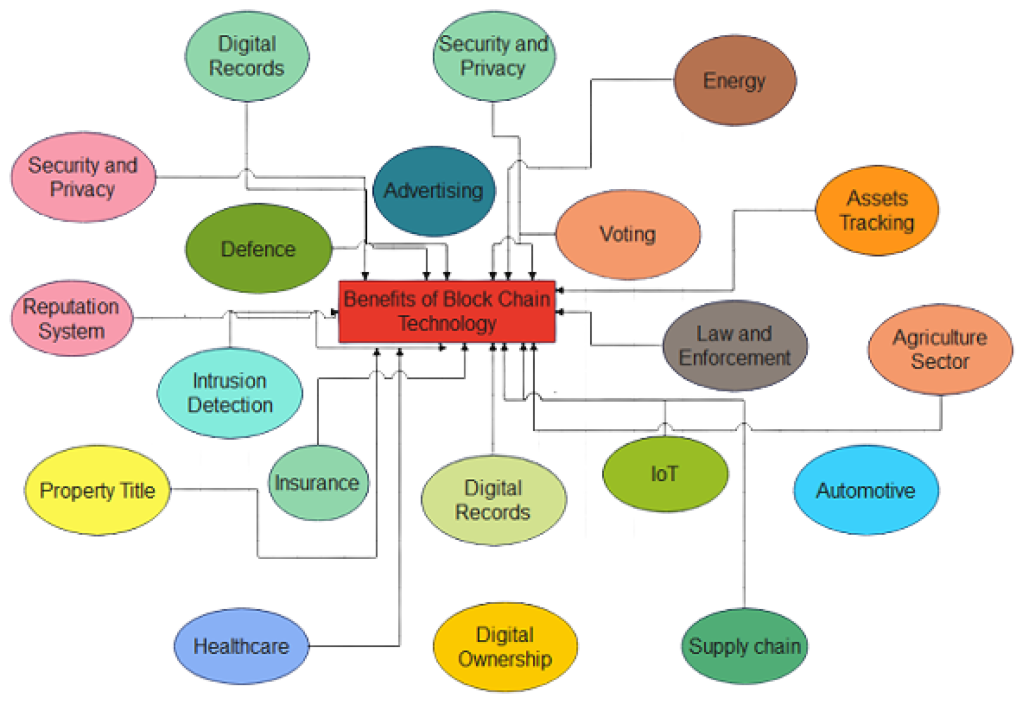
- Blockchain is revolutionizing industries by providing security, transparency, and decentralization.
- While challenges exist, ongoing advancements will drive mass adoption.
- Businesses must stay ahead of blockchain innovations to remain competitive.
📌 Image Placement: (Insert an image summarizing blockchain benefits and its future impact.)