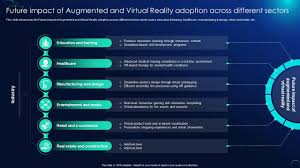
Virtual Reality – Transforming Industries & The Future of Immersion
Virtual Reality (VR) is revolutionizing how we interact with digital environments by providing immersive, computer-generated experiences. From gaming to healthcare, VR is reshaping industries and unlocking new possibilities for entertainment, training, and communication.
Learn more at Red9Systech Virtual Reality Guide.

What is Virtual Reality (VR)?
- VR is a simulated 3D environment that allows users to interact with a digital world through specialized headsets and controllers.
- Unlike traditional screens, VR creates an immersive experience where users feel present in a virtual space.
- Major VR devices include Oculus Quest, HTC Vive, and PlayStation VR.
Read more about Virtual Reality Basics.
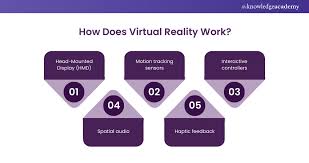
How Does Virtual Reality Work?
- Hardware Components: VR requires head-mounted displays (HMDs), motion sensors, and controllers.
- Software & Content: VR experiences are powered by 3D simulations, AI algorithms, and interactive environments.
- Tracking & Interaction: Advanced motion tracking, haptic feedback, and eye-tracking enhance immersion.
Explore How VR Technology Works.
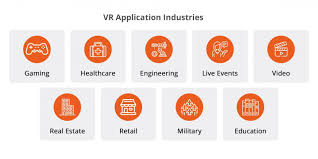
Key Applications of Virtual Reality
- VR enables virtual offices, 3D meetings, and immersive presentations.
- Companies use VR for architectural visualization and design simulations.
1.Gaming & Entertainment
- VR gaming offers 360° experiences with full-body movement and real-time interactions.
- Games like Half-Life: Alyx and Beat Saber showcase the immersive power of VR.
2. Healthcare & Therapy
- VR assists in pain management, physical therapy, and surgical simulations.
- Exposure therapy using VR helps treat phobias, PTSD, and anxiety disorders.
3. Education & Training
- Students experience virtual field trips, interactive labs, and historical reconstructions.
- VR is used for military, medical, and aviation training simulations.
4. Business & Remote Collaboration
Discover more Virtual Reality Use Cases.
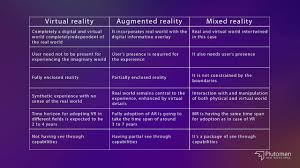
Differences Between VR, AR, and MR
| Feature | Virtual Reality (VR) | Augmented Reality (AR) | Mixed Reality (MR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully immersive digital environment | Overlays digital elements on the real world | Blends digital and real-world elements interactively |
| Hardware | VR headsets (Oculus, HTC Vive) | Smartphones, AR glasses | HoloLens, Magic Leap |
| Example Uses | Gaming, simulations, therapy | Navigation, marketing, AR filters | Industrial training, advanced collaboration |
Learn more about VR vs. AR vs. MR.
Challenges of Virtual Reality
1. Motion Sickness & Discomfort
- Some users experience dizziness and nausea due to VR motion tracking.
2. High Hardware Costs
- VR headsets and powerful computers are expensive, limiting accessibility.
3. Content & Software Development
- Creating realistic, interactive VR experiences requires advanced development tools.
Read about VR Challenges & Solutions.

The Future of Virtual Reality
- Wireless VR & AI-powered experiences will enhance realism and user engagement.
- Haptic feedback and brain-computer interfaces (BCI) will create deeper sensory experiences.
- Metaverse & Virtual Workspaces will revolutionize social interactions and business collaborations.
Stay updated with VR Trends & Future Insights.

Conclusion
- Virtual Reality is reshaping industries, from entertainment to education and healthcare.
- As technology advances, VR accessibility and content development will improve.
- Businesses should explore VR integration to stay ahead in the digital era.
Start exploring Virtual Reality at Red9Systech.