Quantum Computing: Unlocking Powerful Computation
Quantum Computing is rapidly shifting from the realm of theory to real-world impact. By leveraging the laws of quantum mechanics, these machines offer immense processing power, making it possible to solve problems that classical computers can’t handle.
Explore more in our Quantum Insights
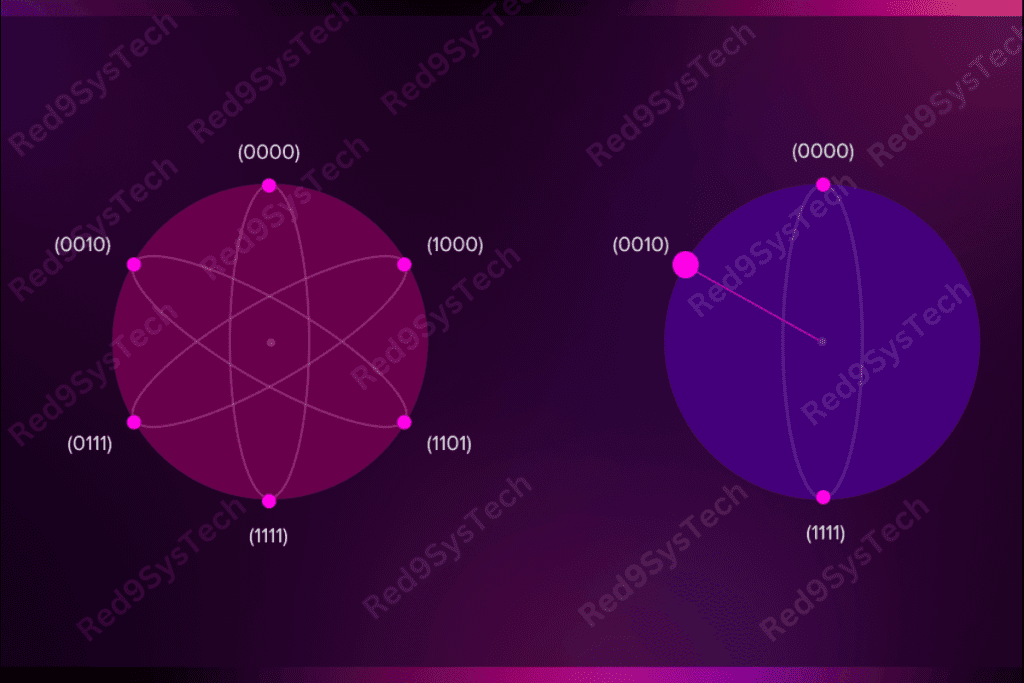
What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum Computing uses qubits—quantum bits—that can exist in multiple states at once, thanks to principles like superposition and entanglement. Unlike traditional bits that are 0 or 1, qubits can be both at the same time, enabling parallelism in computation.
This makes Quantum Computing exponentially more powerful for specific tasks like cryptographic analysis, simulations, and optimization.
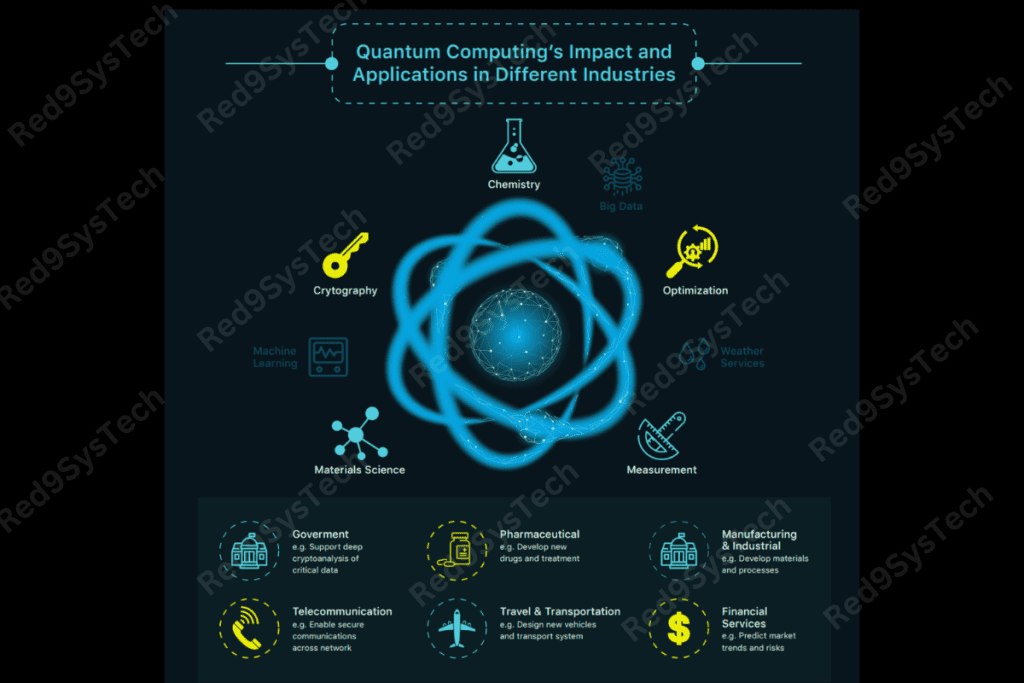
Applications of Quantum Computing
Quantum technology is set to disrupt multiple sectors:
Cryptography
Quantum computers could decrypt today’s most secure encryption algorithms.
This has sparked the rise of quantum-safe encryption techniques.
Drug Discovery & Material Science
Simulating molecular behavior at the quantum level helps discover new medicines faster.
Scientists use quantum models to design advanced materials for clean energy and nanotech.
Financial Modeling
Quantum algorithms improve risk analysis, asset valuation, and portfolio optimization.
Optimization Problems
Quantum systems solve logistic challenges in transportation, manufacturing, and scheduling.
Read more about Quantum technology

Advantages of Quantum Computing
Unmatched Speed
Quantum processors can complete tasks in seconds that would take classical computers years.Energy Efficiency
While still in development, future quantum systems may use significantly less energy.Solving the Unsolvable
Quantum algorithms can tackle complex systems in climate modeling, AI, and cybersecurity.
Challenges in Quantum Computing
Despite its promise, several obstacles remain:
Decoherence
Qubits are extremely sensitive to interference, leading to information loss during calculations.
Error Correction
Quantum error correction requires multiple physical qubits to represent one logical qubit, which increases complexity.
Scalability
Building large, reliable quantum computers is expensive and technically difficult.
Read more about Quantum Limitations.
The Road Ahead for Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is progressing toward practical integration through:
Hybrid Models combining classical and quantum computing.
Cloud Quantum Platforms like IBM Q, Google Quantum AI, and Amazon Braket.
Government & Industry Collaborations investing billions into research and applications.
As breakthroughs continue, businesses will gain access to quantum cloud services, making it possible to solve industry-specific challenges without owning physical quantum hardware.
Stay ahead with us for Trends Blog.
Conclusion
Quantum Computing stands at the edge of a technological revolution. By leveraging the unique behaviors of quantum particles, we can address the world’s most complex problems—from cybersecurity and drug discovery to AI and climate change.
Although challenges remain, its future is promising and filled with innovation. Organizations that start learning and investing in quantum technology today will lead tomorrow’s breakthroughs.
Start your Quantum Journey