Introduction: The Shift Towards Decentralized Computing
Imagine you’re streaming your favorite show, and suddenly, there’s a lag. Or consider a self-driving car that needs to make split-second decisions. In both scenarios, the speed at which data is processed is crucial. Traditionally, data travels to centralized servers (often miles away) for processing, leading to delays. Enter edge computing—a paradigm shift that processes data closer to its source, reducing latency and enhancing real-time decision-making.
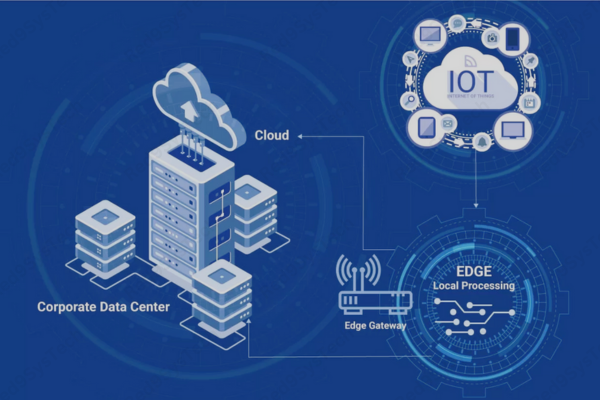
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing involves processing data near its origin, such as sensors, cameras, or local devices, rather than relying solely on centralized data centers. This approach minimizes the distance data must travel, leading to faster processing times and reduced bandwidth usage.
Key Characteristics
Proximity: Data is processed near its source.
Real-time Processing: Enables immediate data analysis and response.
Reduced Latency: Minimizes delays in data transmission.
Bandwidth Optimization: Decreases the amount of data sent over networks.
Why Does Edge Computing Matter?
In our increasingly connected world, the volume of data generated is staggering. According to Gartner, by 2025, 75% of enterprise-generated data will be created and processed outside traditional centralized data centers or cloud environments. This shift is driven by the need for faster data processing, real-time analytics, and the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Explore more blogs related to Edge Computing.
Real-Life Use Cases of Edge Computing
1. Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars rely on real-time data processing to navigate safely. Edge computing allows these vehicles to process data from sensors and cameras instantly, making split-second decisions without relying on distant servers.
2. Healthcare Monitoring
Wearable devices can monitor vital signs and alert healthcare providers in real-time if anomalies are detected. Processing this data at the edge ensures timely interventions, which can be life-saving.
3. Smart Manufacturing
In industrial settings, machinery equipped with sensors can detect anomalies or predict maintenance needs. Edge computing enables immediate processing of this data, reducing downtime and increasing efficiency.
4. Retail Analytics
Retailers can use edge computing to analyze customer behavior in real-time, adjusting promotions or store layouts dynamically to enhance the shopping experience.
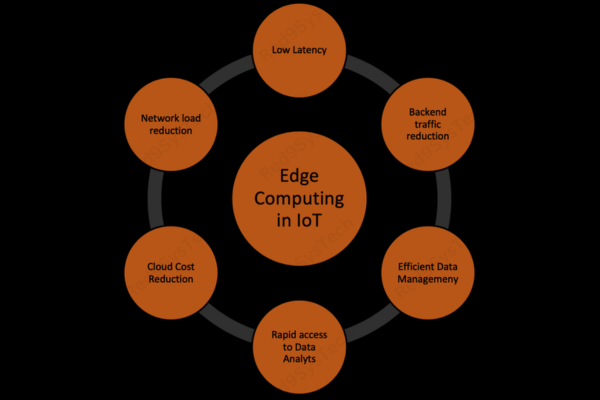
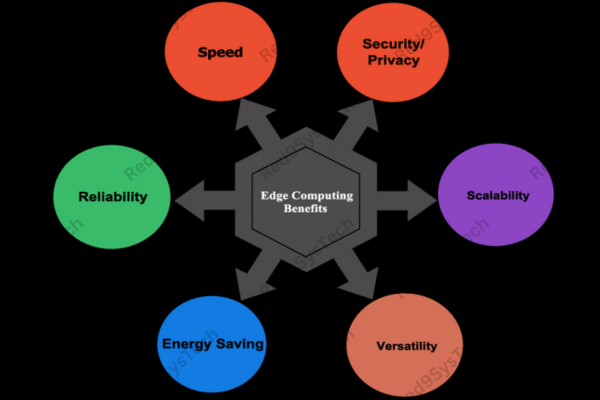
Benefits of Edge Computing
Enhanced Speed: Immediate data processing leads to faster decision-making.
Improved Reliability: Reduces dependency on centralized servers, ensuring continuous operation even during connectivity issues.
Increased Security: Processing data locally minimizes exposure to potential cyber threats.
Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for extensive data transmission and storage infrastructure.
Explore more blogs related to Edge Computing.
Challenges and Considerations
While edge computing offers numerous advantages, it’s essential to be aware of potential challenges:
Security Concerns: Decentralized processing can introduce new security vulnerabilities.
Infrastructure Requirements: Implementing edge computing may require significant investment in local hardware and software.
Data Management: Ensuring data consistency and integrity across multiple edge devices can be complex.
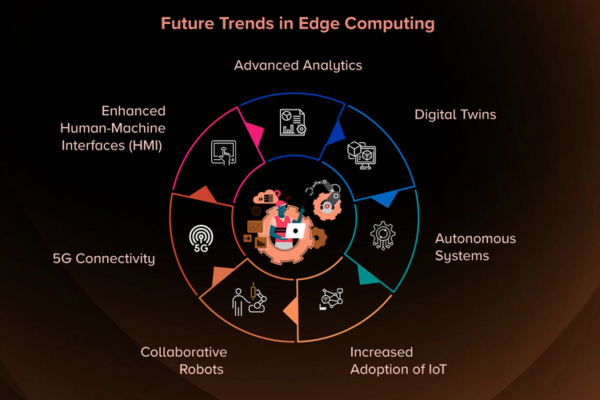
The Future of Edge Computing
As technology evolves, edge computing is poised to become even more integral to various industries. The integration of 5G networks will further enhance its capabilities, enabling faster data transmission and supporting more connected devices. Additionally, advancements in AI and machine learning will allow edge devices to make more sophisticated decisions independently.
Explore more blogs related to Edge Computing.
Getting Started with Edge Computing
For those interested in exploring edge computing:
Assess Your Needs: Determine which operations would benefit from real-time data processing.
Invest in the Right Hardware: Equip your environment with devices capable of local data processing.
Implement Robust Security Measures: Protect your edge devices from potential threats.
Collaborate with Experts: Engage with professionals who specialize in edge computing to ensure a smooth implementation.