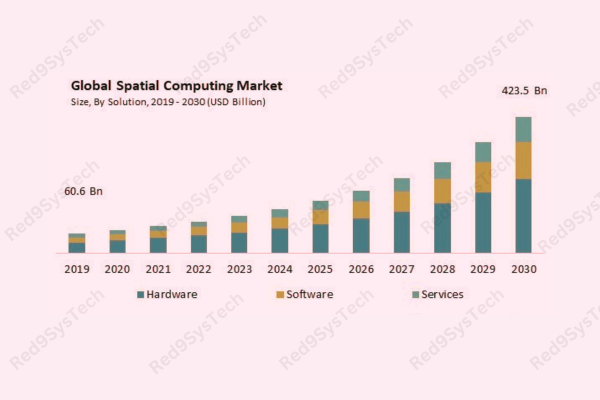
Introduction: The Rise of Spatial Computing
Picture this: You’re wearing smart glasses, and with a simple glance at a product in a store, digital information appears in your field of view—price comparisons, customer reviews, even virtual try-ons. This isn’t science fiction anymore. Welcome to the world of Spatial Computing.
Spatial computing is revolutionizing how we interact with technology by seamlessly blending the physical and digital realms. It’s not just for gaming or entertainment; industries like healthcare, education, retail, and manufacturing are embracing it for practical, game-changing applications.

Understanding Spatial Computing
Spatial Computing refers to technologies that enable machines to understand, interact with, and manipulate objects and environments in the physical world through digital means. It leverages AR (Augmented Reality), VR (Virtual Reality), AI, IoT, and computer vision to create immersive, interactive experiences.
In simple terms, spatial computing is about making computers “aware” of the physical space around them and allowing users to interact with digital information as if it were part of the real world.
Key Components of Spatial Computing
Augmented Reality (AR): Overlaying digital information onto the physical world.
Virtual Reality (VR): Immersing users in a fully digital environment.
Mixed Reality (MR): Combining real and virtual worlds to create new environments.
3D Mapping & Sensors: Capturing spatial data to understand surroundings.
AI & Machine Learning: Enabling context-aware interactions and intelligent responses.
Edge Computing & IoT: Processing data in real-time for low-latency experiences.
Why Spatial Computing Matters in 2025
The digital experience is evolving beyond screens. Consumers and businesses demand more intuitive, immersive, and natural interactions with technology. Spatial computing delivers on that by:
Enhancing User Experience: More engaging and interactive interfaces.
Boosting Productivity: Hands-free access to information in industrial, medical, and fieldwork scenarios.
Revolutionizing Training & Education: Simulations and virtual environments for effective learning.
Transforming Retail & Marketing: Virtual try-ons, in-store AR experiences, and personalized advertising.
Enabling Smart Environments: Intelligent spaces that respond to human presence and behavior.
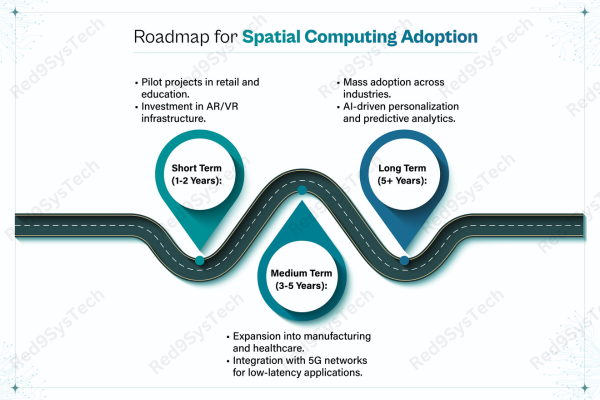
Implementing Spatial Computing: A Practical Roadmap
1. Assess Use Cases & Business Needs
Identify where spatial computing adds real value (customer experience, training, remote support).
Align with business goals and customer expectations.
2. Choose the Right Technology Stack
Select AR/VR platforms, AI tools, sensors, and devices suitable for your industry.
Ensure compatibility with existing IT infrastructure.
3. Develop & Test Prototypes
Start with small, focused pilots to validate feasibility and user adoption.
Gather feedback and iterate quickly.
4. Invest in Skills & Training
Upskill teams in AR/VR development, 3D modeling, AI integration, and spatial design principles.
Foster collaboration between developers, designers, and business stakeholders.
5. Focus on Data & Privacy
Implement robust data protection measures.
Ensure compliance with privacy regulations when collecting and processing spatial data.
6. Scale with a Long-Term Vision
Plan for scalability across multiple use cases and departments.
Continuously innovate based on user feedback and technological advancements.
Real-Life Use Case: Spatial Computing in Healthcare
A leading healthcare provider integrated spatial computing for remote surgery assistance and medical training. Using AR headsets, surgeons could overlay patient data during procedures, consult with remote experts in real-time, and train new doctors using realistic 3D simulations.
Results:
Reduced surgery errors by 30%.
Improved training efficiency and retention.
Enhanced patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Best Practices for Spatial Computing Success
User-Centric Design: Prioritize ease of use and intuitive interfaces.
Cross-Functional Teams: Blend technical and creative expertise for innovative solutions.
Agile Development: Adopt iterative approaches for continuous improvement.
Measure Impact: Track KPIs like user engagement, ROI, and productivity gains.
Stay Updated: Keep pace with evolving AR/VR devices, AI advancements, and industry standards.
Conclusion: The Future is Spatial
Spatial computing is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s the present and the future of digital interaction. By bridging physical and digital worlds, it opens up endless possibilities for businesses to innovate, engage, and excel.
Stay Update in our Red9SysTech