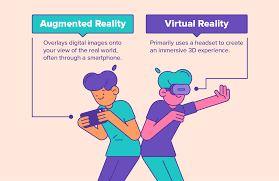
What is Augmented Reality (AR)?
- AR enhances the real world by overlaying computer-generated visuals, sounds, and information.
- Unlike VR, AR does not replace reality but adds digital elements to it.
- Major AR devices include Microsoft HoloLens, Magic Leap, and AR-enabled smartphones.
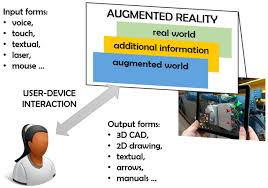
How Does Augmented Reality Work?
1. Hardware Components
- AR requires smart glasses, mobile AR applications, and head-mounted displays (HMDs).
2. Software & Content
- AR experiences are powered by computer vision, AI algorithms, and spatial computing.
3. Tracking & Interaction
- Marker-based AR, markerless AR, and LiDAR scanning enhance accuracy and real-world interaction.
Key Applications of Augmented Reality
AR enables immersive product visualization, remote assistance, and real-time navigation.
1. Gaming & Entertainment
- AR gaming offers interactive digital overlays in real-world environments.
- Games like Pokémon GO and Minecraft Earth showcase the immersive power of AR.
2. Healthcare & Surgery
- AR assists in surgical navigation, medical training, and diagnostics.
- AR headsets like Microsoft HoloLens provide real-time imaging for doctors.
3. Education & Training
- AR brings interactive textbooks, virtual dissections, and anatomy simulations to life.
- Used in aviation, military, and industrial training simulations.
4. Retail & E-Commerce
- AR-powered virtual try-ons allow customers to preview clothing, makeup, and furniture.
- Brands like IKEA Place and Sephora Virtual Artist use AR for immersive shopping experiences.
Differences Between AR, VR, and MR
| Feature | Augmented Reality (AR) | Virtual Reality (VR) | Mixed Reality (MR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Overlays digital elements on the real world | Fully immersive digital environment | Blends digital and real-world elements interactively |
| Hardware | Smartphones, AR glasses | VR headsets (Oculus, HTC Vive) | HoloLens, Magic Leap |
| Example Uses | Navigation, marketing, AR filters | Gaming, simulations, therapy | Industrial training, advanced collaboration |
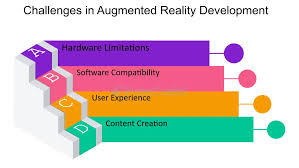
Challenges of Augmented Reality
1. Limited Field of View
- AR glasses have restricted display areas, affecting user immersion.
2. Hardware & Processing Power
- AR requires high-performance processors and advanced sensors.
3. Privacy & Data Security
- AR applications collect real-world data, raising security concerns.
The Future of Augmented Reality
- AI-powered AR and 5G connectivity will improve real-time responsiveness.
- Holographic displays and AR contact lenses will enhance user experience.
- Metaverse & AR Cloud will drive new social, retail, and workplace applications.
Conclusion
- Augmented Reality is reshaping industries, from retail and healthcare to education and business.
- As technology advances, AR adoption and development will continue to grow.
- Businesses should explore AR integration to stay ahead in the digital era.