MySQL: A Complete Guide to Database Management & Queries
MySQL is a powerful open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) used for storing, retrieving, and managing structured data. It is widely used in web applications, enterprise systems, and cloud-based services.
Discover more at RedSysTech MySQL Guide.

What is MySQL?
- MySQL is a structured query language (SQL)-based RDBMS.
- Developed by Oracle Corporation, it is fast, reliable, and scalable.
- Used for storing, retrieving, and managing structured data.
- Supports ACID compliance, transactions, and multi-user access.
Learn more at MySQL Official Documentation.
Why Use MySQL?
- Open-source & Free – No licensing costs.
- High Performance – Optimized for fast query execution.
- Scalability – Supports small to enterprise-level applications.
- Security – Implements encryption, access control, and backups.
- Cross-Platform – Runs on Windows, Linux, macOS, and cloud servers.
Explore MySQL Features.
MySQL Basic Commands & Queries
1. Install MySQL on Windows
- Download MySQL from mysql.com.
- Follow the installation wizard and select MySQL Server & Workbench.
2. Install MySQL on Linux (Ubuntu/Debian)
bash
sudo apt update
sudo apt install mysql-server
sudo systemctl start mysqlLearn How to Install MySQL.
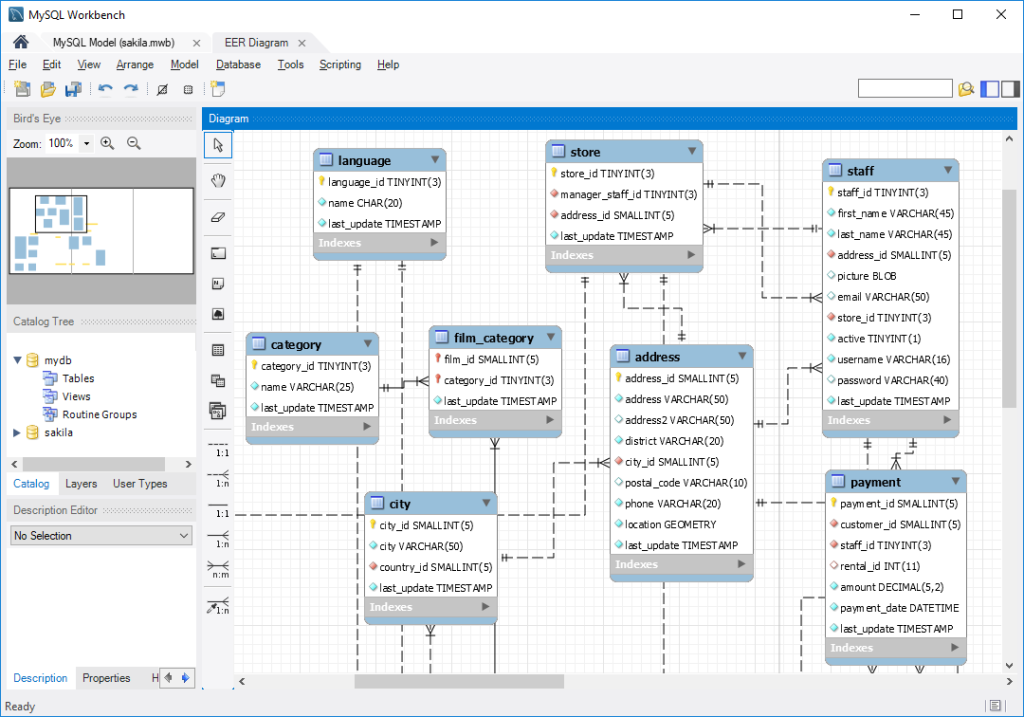
Installing MySQL on Windows & Linux
1. Creating a Database
sql
CREATE DATABASE CompanyDB;
2. Using a Database
sql
USE CompanyDB;
3. Creating a Table
sql
CREATE TABLE Employees (
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(100),
position VARCHAR(50),
salary DECIMAL(10,2)
);
4. Inserting Data
sql
INSERT INTO Employees (name, position, salary)
VALUES ('Alice', 'Developer', 70000);
5. Retrieving Data
sql
SELECT * FROM Employees;
6. Updating a Record
sql
UPDATE Employees
SET salary = 75000
WHERE name = 'Alice';
7. Deleting a Record
sql
DELETE FROM Employees
WHERE name = 'Alice';
MySQL Joins – Combining Data from Multiple Tables
| Join Type | Description | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| INNER JOIN | Returns matching records in both tables | Fetch employees and their departments |
| LEFT JOIN | Returns all records from the left table, matching ones from the right | List all employees, even if they have no department |
| RIGHT JOIN | Returns all records from the right table, matching ones from the left | List all departments, even if no employee is assigned |
| FULL OUTERJOIN | Returns all records from both tables | Get a complete view of employees and departments |
MySQL Indexing & Performance Optimization
- Indexes improve query performance by allowing faster lookups.
- Use EXPLAIN to analyze and optimize queries.
- Use LIMIT to reduce data retrieval time.
Example: Creating an Index
sql
CREATE INDEX idx_employees_name ON Employees(name);
Example: Query Optimization
sql
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM Employees WHERE name = 'Alice';
MySQL Security Best Practices
- Use Strong Passwords – Secure database logins.
- Limit User Privileges – Restrict unauthorized access.
- Enable SSL Encryption – Protect data in transit.
- Perform Regular Backups – Prevent data loss.
- Prevent SQL Injection – Use prepared statements.
Example: Creating a Secure User
sql
CREATE USER 'admin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'StrongPassword!';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON CompanyDB.* TO 'admin'@'localhost';Check out MySQL Security Guide.
MySQL vs Other Databases (PostgreSQL, SQL Server, MongoDB)
| Feature | MySQL | PostgreSQL | SQL Server | MongoDB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Relational | Relational | Relational | NoSQL |
| Speed | Fast | Moderate | Fast | Very Fast |
| Best For | Web Apps | Advanced Queries | Enterprise Apps | NoSQL Apps |
| ACID Compliance | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
Career Opportunities for MySQL Professionals
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Database Administrator (DBA) | Manages database security, backups, and optimization. |
| MySQL Developer | Develops database-driven applications and APIs. |
| Data Analyst | Uses SQL for business intelligence and reporting. |
Conclusion
- MySQL is a widely used database system for applications of all sizes.
- It supports fast queries, transactions, security, and scalability.
- Learning MySQL opens doors to high-paying database careers.
Start learning MySQL Today.